Developing AI technologies in healthcare and promoting better healthcare services using AI technologies along with stakeholders
AI in healthcare is being promoted by a wide range of stakeholders, including the government, industry, and academia (relevant ministries, companies, and university hospitals), as a means of providing patients with faster and more accurate healthcare services.
In the context of the development of AI technologies in healthcare, the AIDE project aims to develop an engagement platform where a variety of stakeholders can be involved in shaping this process to draw on a range of knowledge and experience. In this process, we hope to describe the current involvement landscape around AI in healthcare and identify key concerns of stakeholders.
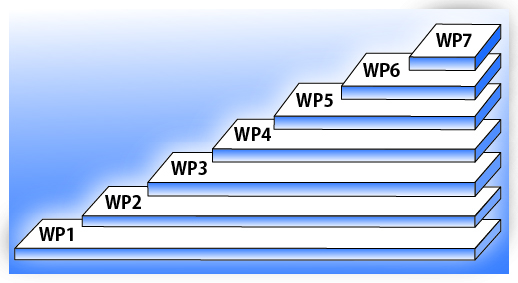
The AIDE Project is made up of different ‘work packages’
We hope to achieve the aims of the AIDE project through activities carried out within seven work packages (WPs). They include the initial strategic planning (WP1), the establishment of a ‘Patient and Public Involvement Panel (PPIP)’ (WP2), a scoping review and Twitter study that provide a foundation for empirical research (WP3), empirical research (WPs 4, 5 and 6), and designing a stakeholder involvement platform to develop AI in healthcare (WP7), the final stage of the project.
WP1: Developing strategies for dissemination of information and publicity between Japan and the UK research team
AIDE is a collaborative research project between the University of Oxford in the UK and Osaka University in Japan.
Research teams from both universities developed strategies early on to work together to manage the overall progress of the project, as well as to disseminate information to stakeholders by creating websites.
As part of the AIDE research project, both the UK and Japan teams established advisory boards of external experts.

WP2: Establishing a Patient and Public Involvement Panel (PPIP)
As part of the AIDE project, PPIPs have been organised in Japan and the UK, which bring important perspectives to the research.
The AIDE project considers that it is important to involve patients and citizens who have not necessarily been involved previously in activities connected to the development and implementation of AI in healthcare. To this end, a PPIP was set up as part of WP2 early on in the project in order to incorporate patient and public perspectives.
In response to a public call for participants, 11 patients and citizens have been involved in the AIDE project in Japan, and the PPIP members have been actively ensuring the inclusion of the views and opinions of patients and citizens in all AIDE work packages.
PPIP members have been provided with the opportunity to learn about AI in healthcare and gain a deeper understanding of the topic through lectures given by researchers and experts in the field. This has enabled them to engage fully in the discussion throughout the project.
The research team has held regular meetings with PPIP members. These meetings have been aimed at co-producing WP5 and WP6. In addition, we have met with the PPIP to discuss our analysis of results from WP3 to WP7, thus bringing in the patient and public perspective into the research process.
The PPIP plays a key role in the AIDE project as the core and driving force along with the research team.
WP3: Scoping review and Twitter study
A scoping review was conducted to identify previous research and reports concerned with stakeholder involvement in the development and introduction of AI in the healthcare sector. We analyzed the contents of 27 articles and reports to identify which stakeholders were being involved in activities, either as facilitators or participants, the methodologies that were being used, and the outcomes.
The Twitter study was conducted to identify what kind of public discourse was being generated in this social media space around AI in healthcare and to judge the sentiment (positive, negative or neutral) towards this disruptive change to health care systems and delivery. We collected Japanese and English Tweets over a short period early on in the project and then analysed the tweets in a variety of ways.
Findings from the Twitter study will be published soon.
WP4: Identifying stakeholders in the introduction of AI into healthcare
In WP4, we worked with Osaka University Hospital and University of Oxford related hospitals to identify stakeholders involved in the development of AI technologies for healthcare. We know that doctors and other health care professionals are involved, but which groups are particularly affected? At the same time, where is the innovation in this field coming from?
The research team brought together AI medical experts from Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust and Osaka University Hospital for a roundtable discussion. The purpose of this roundtable meeting was to discuss the current status and challenges in the development and implementation of AI in healthcare.
Roundtable discussions provided insights into AI clinical experts’ knowledge and perspectives about the different types of AI technologies being developed or introduced into the healthcare sector, how these AI technologies are affecting current clinical settings, and who the affected stakeholders are.
WP5: Focus group study
In WP5, stakeholders identified in WP3 and WP4 were recruited as participants. Different stakeholder groups were interviewed in small groups according to their respective positions.
During the focus group interview, participants were presented with scenarios of AI applications in healthcare, and they were asked to express their opinions about the merits and demerits of this use of AI, as well being asked to address the broader topic of stakeholder involvement in AI development and implementation in healthcare.
The examples used in the focus group study for WP5 were developed with input from WP4 experts and AI medical experts from the AIDE project, and were presented to AI medical experts and PPIP members for feedback and revision.
Click here to access the updates about the development of examples used in WP5.
https://en.aide.osaka.jp/2021051001/
https://en.aide.osaka.jp/2021101501/
https://en.aide.osaka.jp/2022011401/
WP6: Ranking statements around AI in healthcare
Based on findings from WP2-5, we are developing a dataset of statements about AI development in healthcare – issues that need to be considered, points of concern, the importance of stakeholder involvement in development and implementation. Both the Osaka and Oxford teams are developing the statements together. The dataset of statements will be presented to the PPIPs and other experts for validation.
A statement captures an opinion. For example, “AI will improve clinical diagnostics and detection in the near future”.
The participants are asked to rate the statements in terms of importance and relevance and explain their reasoning in WP6.
The empirical study of WP6 seeks to clarify “what stakeholders consider to be the most important aspects of implementing AI in healthcare, what needs attention, and what are the priorities for sustainable stakeholder involvement in AI in healthcare.”
WP7: Designing a platform for a wide range of stakeholders to be involved in the development and implementation of AI technologies in healthcare
Based on the results of earlier work packages, the AIDE project team will create a prototype for establishing a platform for the involvement of a wide range of stakeholders in decision-making in the development and implementation of AI technologies in healthcare. In this way, the AIDE project will contribute to the future development of AI healthcare and ensures possible benefits of AI in healthcare for public health and well-being.
We will clarify whether the following types of involvement are possible and what is needed to ensure their sustainability.
Some examples of possible involvement at the platform
1. To facilitate public discussion around AI healthcare through information sharing.
Patients and citizens are provided with information on initiatives for the development of AI in healthcare, specific cases of implementing AI in healthcare, and seminars on AI in healthcare in websites, newsletters, and other media.
It is expected that information sharing will facilitate informed and transparent discussions and debates about AI healthcare among various stakeholders.
2. To facilitate interactions between various stakeholders and provide easy access to consultations
When designing AI for healthcare and introducing AI in healthcare, AI developers and healthcare practitioners can obtain direct feedback from patients and citizens. Patients and citizens can discuss expectations of AI in healthcare and concerns about it with healthcare practitioners and AI developers. In addition, the development of AI for healthcare can be discussed by AI developers with healthcare practitioners.
3. To facilitate involvement of diverse stakeholders and contribute to the development of AI in healthcare and ensure possible benefits to individuals and for the public good
Various issues related to AI healthcare and solutions to the issues can be discussed in a two-way dialogue between a wide range of stakeholders during the policymaking and development processes.
It is hoped that this platform will be able to engage a wide range of stakeholders, including policymakers, medical and technological experts, professionals, patients, and citizens. By identifying and addressing emerging concerns as early as possible through involvement of stakeholders, the platform is expected to contribute to the sustained development of AI in healthcare and its benefits for all.

